Confusion Matrix: An introduction
In Classification, a Confusion Matrix provides a Visual comparison of true vs. predicted classes.
The following complete Python program shows how to create a Confusion Matrix:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load sample data
data = load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
# Split data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# Train a classifier (Random Forest in this case)
clf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
# Compute the confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
# Plot the confusion matrix
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues', xticklabels=data.target_names, yticklabels=data.target_names)
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.show()
The code does the following tasks:
- Imports Necessary Libraries: We import the required libraries, including
scikit-learnfor the machine learning model andseaborn,matplotlibfor visualization. - Generates Sample Data: We use the Iris dataset as an example. It is a classic dataset for classification.
- Trains a Classifier: We use a Random Forest classifier for this example.
- Makes Predictions: We predict the labels for the test set.
- Computes the Confusion Matrix: We calculate the confusion matrix using scikit-learn’s
confusion_matrixfunction. - Visualizes the Confusion Matrix: We use
seabornto create a heatmap for the confusion matrix, making it easy to interpret.
Running it generates the following output:
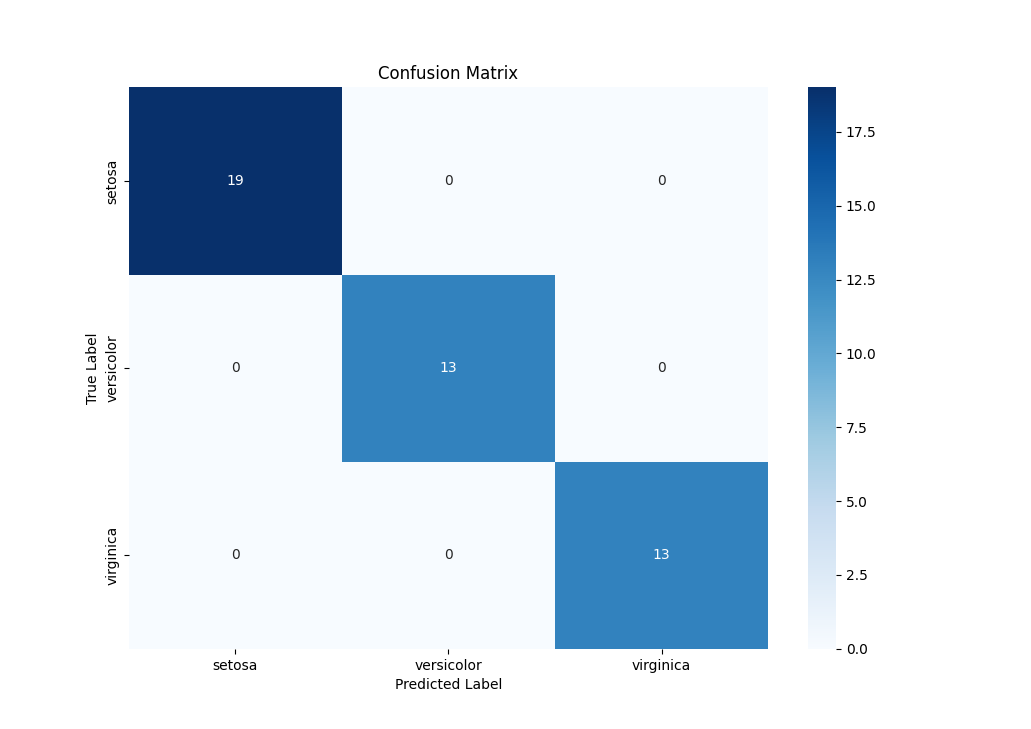
How to Read the Confusion Matrix Link to heading
- Rows: True labels.
- Columns: Predicted labels.
- The labels (Setosa, Versicolor, Virginica) correspond to the classes in the Iris dataset.